The equation is generally written with liabilities appearing before owner’s equity because creditors usually have to be repaid before investors in a bankruptcy. In this sense, the liabilities are considered more current than the equity. This is consistent with financial reporting where current assets and liabilities are always reported before long-term assets and liabilities. Shareholder Equity is equal to a business’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It can be found on a balance sheet and is one of the most important metrics for analysts to assess the financial health of a company. Since the balance sheet is founded on the principles of the accounting equation, this equation can also be said to be responsible for estimating the net worth of an entire company.

The cash (asset) of the business will increase by $5,000 as will the amount representing the investment from Anushka as the owner of the business (capital). Double-entry bookkeeping is a system that records transactions and their effects into journal entries, by debiting one account and crediting another. Now, there’s an extended version of the accounting equation that includes all of the elements (described in the section above) that comprise the Owner’s Equity.
Double entry bookkeeping system
Income and expenses relate to the entity’s financial performance. Individual transactions which result in income and expenses being recorded will ultimately result in a profit or loss for the period. The term capital includes the capital introduced by the business owner plus or minus any profits or losses made by the business. Profits retained in the business will increase capital and losses will decrease capital.
For example, when a company borrows money from a bank, the company’s assets will increase and its liabilities will increase by the same amount. When a company purchases inventory for cash, one asset will increase and one asset will decrease. Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction, the accounting system is referred to as the double-entry accounting or bookkeeping system. Examples of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid insurance, investments, land, buildings, equipment, and goodwill.
3 Examples of Equity
A single interface gives you access to all remarkable features, https://www.bookstime.com/ including the ability to add products, services, and inventory.
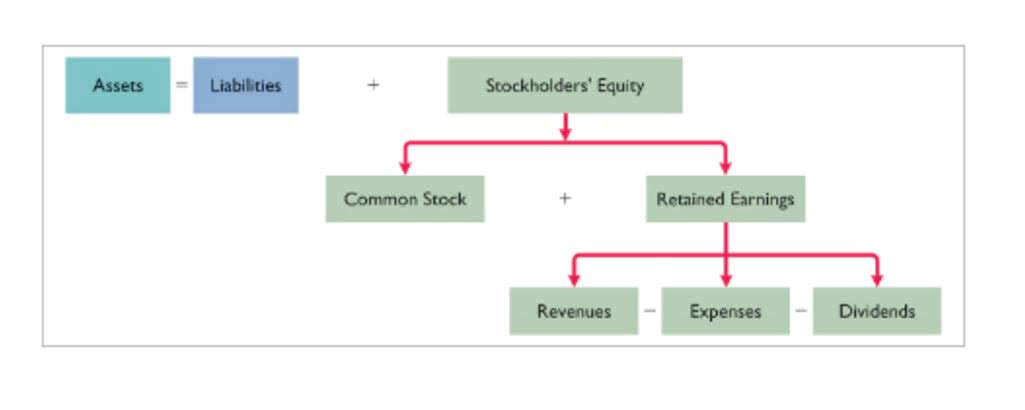
The accounting formula is a fundamental principle of double-entry bookkeeping. The equation states that the total assets of a company must be equal to the total liabilities plus owner’s equity. This equation ensures that all transactions are accounted for and provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at any given moment. In a corporation, capital represents the stockholders’ equity. Thus, the accounting formula essentially shows that what the firm owns (its assets) has been purchased with equity and/or liabilities.
AccountingTools
The asset, liability, and shareholders’ equity portions of the accounting equation are explained further below, noting the different accounts that may be included in each one. Companies compute the accounting equation from their balance sheet. They prove that the financial statements balance and the double-entry accounting system works. The company’s assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and equity.
- These can be in the form of loans, accounts payable to suppliers, or other accrued expenses.
- While trying to do this correlation, we can note that incomes or gains will increase owner’s equity and expenses, or losses will reduce it.
- This equation should be supported by the information on a company’s balance sheet.
- The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
- Double-entry accounting is a system that ensures that accounting and transaction equation should be equal as it affects both sides.
- Your bank account, company vehicles, office equipment, and owned property are all examples of assets.
